The overall computing power of the Bitcoin network has dropped by 15% from its peak. Have miners all switched to AI?
Original Title: "Bitcoin Network Hashrate Drops 15% from Peak, Have Miners Been Driven to AI?"
Author: ChandlerZ, Foresight News
Bitcoin's hashrate has grown approximately tenfold since 2020 but has seen a relatively significant decline in recent months.
Data shows that Bitcoin network hashrate has fallen by about 15% from its October peak, with miners capitulating for nearly 60 days. The average network hashrate dropped from around 1.1 ZH/s in October to approximately 977 EH/s, indicating that miners are shutting down machines or surrendering as profitability declines.
Moreover, Glassnode’s Hash Ribbon indicator reversed on November 29. This metric tracks short-term and long-term hashrate trends to reflect miner capitulation. Currently, short-term supply pressure in the Bitcoin market may increase further, and Bitcoin mining difficulty is expected to decrease for the seventh time in eight adjustments, dropping to around 139 T on January 22.
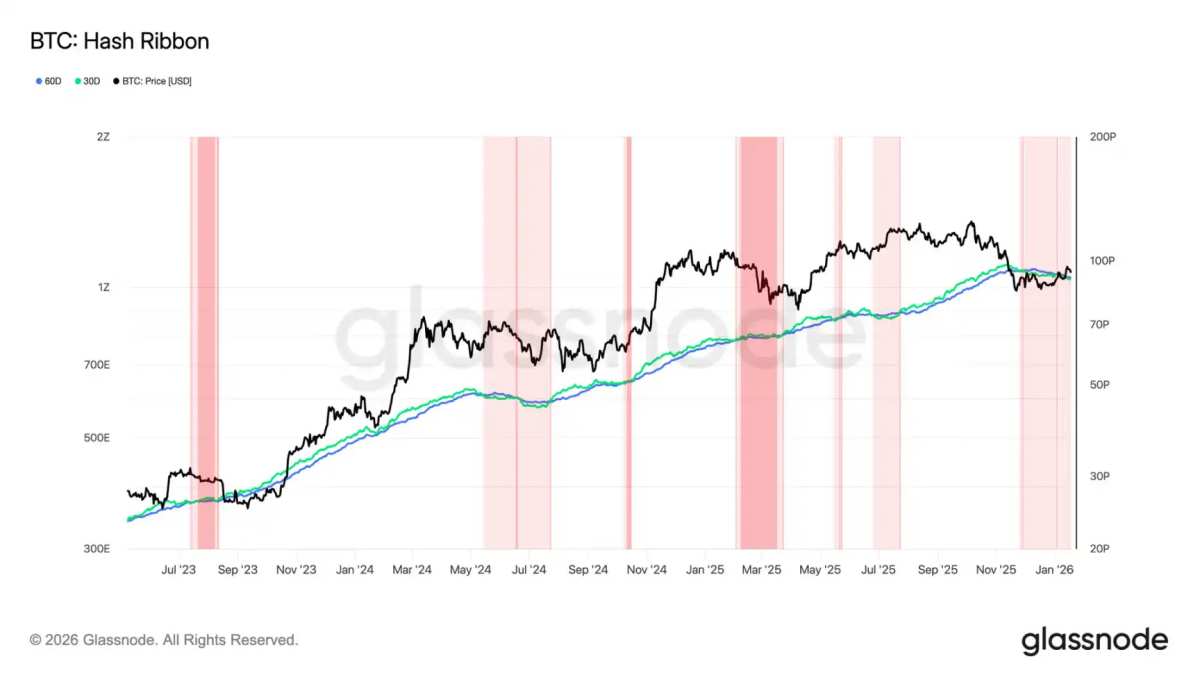
 JPMorgan stated that Bitcoin network hashrate decreased by about 3% month-on-month to 1045 EH/s in December 2025, slightly easing miner competition, but mining profitability continues to decline.
JPMorgan stated that Bitcoin network hashrate decreased by about 3% month-on-month to 1045 EH/s in December 2025, slightly easing miner competition, but mining profitability continues to decline.
However, data shows that miners’ average daily block reward income per EH/s in December 2025 was $38,700, a 7% decrease from November and a 32% year-on-year drop, reaching an all-time low.
A VanEck report analysis suggests that the Bitcoin mining industry is experiencing significant pressure. On one hand, periodic halving of block subsidies causes miners' revenue to drop in a 'step-like' manner; on the other hand, since 2020, the network-wide hashrate has expanded at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 62%. To avoid being phased out, miners must continuously invest CAPEX to increase their hashrate. If Bitcoin prices fail to offset the decline in subsidies and rising costs per unit due to increased hashrate, miner profitability will be systematically compressed.
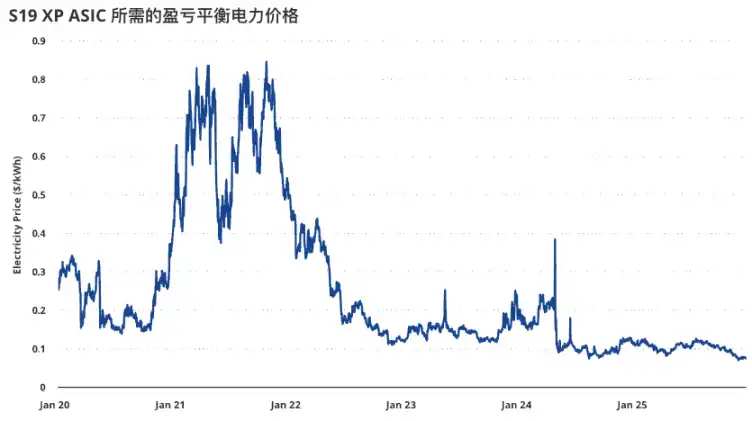
The deterioration in miner profitability can be clearly observed through the breakeven electricity price. Taking the 2022-generation miner S19 XP as an example, its breakeven electricity price fell from approximately $0.12/kWh in December 2024 to about $0.077/kWh in December 2025. This indicates that under the recent weakening of BTC prices, the marginal economics of mining have significantly worsened, increasing the industry’s reliance on low-cost electricity resources, economies of scale, and operational efficiency.
Despite the cumulative growth of approximately 10 times in the network's total computing power since 2020, the 30-day moving average indicates a decline of about 4% in network computing power over the past 30 days, marking the largest drop since April 2024. Meanwhile, supply-side disruptions are also affecting computing power, such as the shutdown of approximately 1.3GW of capacity at mining farms in Xinjiang due to regulatory inspections, with an estimated 400,000 mining machines being taken offline.
A report by Guojin Securities shows that by the third quarter of 2025, the mining cost for U.S.-listed companies, including depreciation, has risen to $112,000, higher than the current price of Bitcoin. Cryptocurrency mining companies own computing power infrastructure near major metropolitan areas that is already electrified and equipped with high communication bandwidth, with electricity costs generally ranging between 3~5 cents per kilowatt-hour, making them naturally suitable for engaging in AI cloud service businesses. With the growing demand for AI computing power, the transition of cryptocurrency mining operations to AI data centers is inevitable.
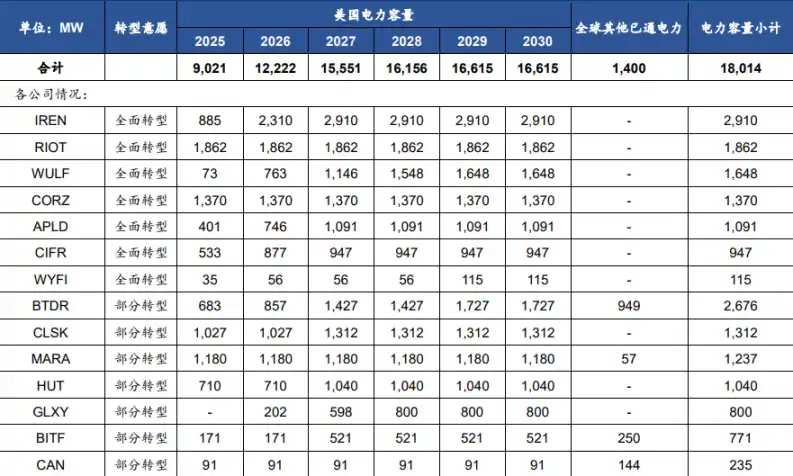
Fourteen major U.S.-listed mining companies are expected to reach a power capacity of 15.6GW by 2027, with their transformation business models primarily focused on cloud computing leasing and IDC power leasing.
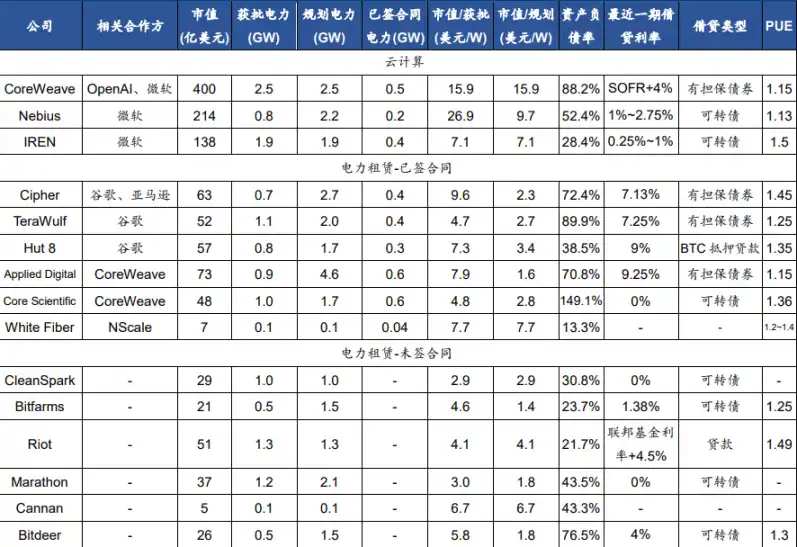
The cryptocurrency mining farms transitioning to AI data centers mainly adopt two business models.
One model resembles CoreWeave and Nebius, which procure chips for cloud computing leasing; IREN currently adopts this business model. IREN’s gross power capacity is 2.91GW, corresponding to approximately 1.9GW of core capacity, with its market capitalization per watt lower than that of CoreWeave and Nebius. It has already entered into a collaboration with Microsoft involving 200MW of core capacity.
The other model is similar to the IDC power leasing approach, where only the usage rights of the data center building and power capacity are leased, while servers and electricity fees are borne by the tenants. Currently, most cryptocurrency mining operations adopt this hosting model. Some companies have signed leasing contracts with firms like Google, Amazon, and CoreWeave, while others, due to their later transitions, are still seeking partners.
However, the VanEck report also suggests that a decline in the hash rate may actually be a positive factor. By comparing the 30-day change in Bitcoin computing power since 2014 with the expected return over the next 90 days, it finds that when Bitcoin computing power declines, the likelihood of a positive expected return is higher than when computing power increases. Moreover, when Bitcoin computing power decreases, the average expected return over 180 days is approximately 30 basis points higher than when computing power rises.
When the compression of computing power persists for an extended period, forward-looking returns tend to be more frequent and of greater magnitude. Since 2014, out of 346 days when the 90-day computing power growth was negative, the probability of a positive 180-day Bitcoin forward return was 77%, with an average return of +72%. In addition, the probability of a positive 180-day Bitcoin forward return is approximately 61%, with an average return of +48%.
Therefore, historically, purchasing BTC when the 90-day hash rate growth is negative has been shown to increase the expected 180-day return by 2400 basis points.
Even during periods of weaker economic conditions, many participants continue to engage in mining. Short-term profitability pressures and fluctuations in computational power are more likely to accelerate industry consolidation and centralization, but this does not necessarily imply a long-term decline in the mining sector.
Content Original Link:
" target="_blank">



































































