ABS publishes safety insights for ammonia as a fuel
The American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) has published the “Safety Insights for Ammonia as a Marine Fuel” report, highlighting findings of ABS research into the performance of ammonia on board.
As stated, ABS performed computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations using tools to quantitatively assess the risks associated with ammonia dispersion in accidental leakage scenarios. Furthermore, engineers examined realistic bunkering situations such as ship-to-ship, terminal-to-ship and truck-to-ship, as well as ammonia dispersion from the vessel due to a leakage incident in the engine room.
While the use of ammonia as a marine fuel is new, the seaborne transportation of ammonia as cargo is not. Ammonia is also commonly used on board vessels as a refrigerant. All the necessary practices for the safe handling of ammonia on board, including operational and safety procedures, are well known in marine liquefied gas industries and accepted by crew and operators.
However, because most of this experience is concentrated in a specific segment of the maritime industry, extending the use of ammonia as a fuel to a broader range of vessels will introduce new risks. Detailed training requirements will need to be in place for safe operation for a larger pool of mariners, and specific regulations will need to be developed to ensure safe adoption.
Ammonia dispersion in the engine room
Computational fluid dynamics can be used to predict the behavior of an ammonia plume due to an accidental release in the engine room. Current research on engine room release could have a range of outcomes on ammonia-fueled vessel design, such as the arrangement of ventilation, the placement of sensors or the design of evacuation routes.
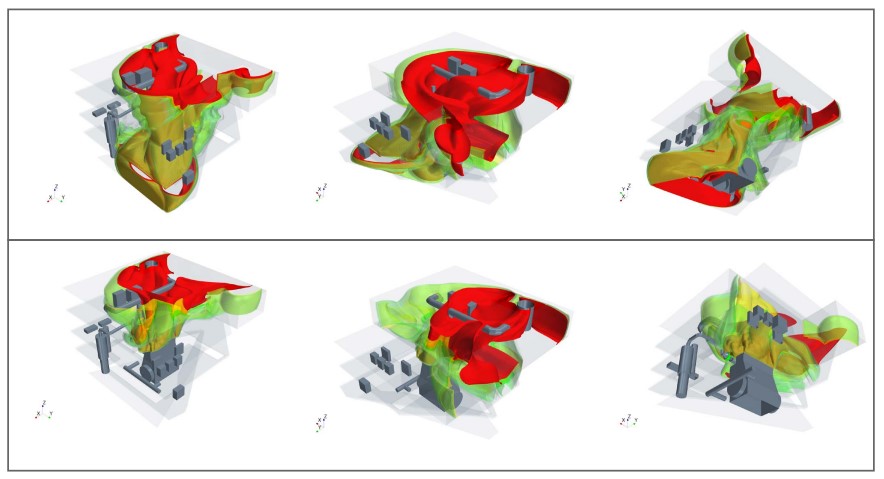
Credit: ABS
Figure 2 illustrates the ammonia dispersion patterns in the engine room. The ventilation rate is set to a typical value of air changes per hour, but the ventilation and leakage direction are some of the study parameters. For demonstration, a mainly upward ventilation direction (i.e., from the lower decks to the higher decks) is assumed.
The simulation results reveal that the release of ammonia perpendicular to the air flow will have less impact on the engine room space, while its release against the air flow tends to have a broad impact by filling nearly all deck levels with significant ammonia concentrations. Both cases indicate that the ammonia concentration could reach 10 percent of the lower explosive limit (LEL), leading to a potential fire risk.
Furthermore, high concentrations could be attained in areas with poor ventilation, such as corners or the space underneath the deck floors.
In addition to CFD simulation analysis, ABS leveraged industry best practices and advancements in software and hardware, including acoustic cameras for detecting and visualizing ammonia leakage to provide a thorough, three-part framework for owners and operators evaluating ammonia as a cleaner fuel source.
This approach requires a comprehensive strategy that addresses the following three interconnected areas:
1. Proactive Regulatory Engagement and Risk Anticipation: The first crucial step involves anticipating and actively engaging with future regulatory developments pertaining to ammonia as a marine fuel. This requires:
- Identifying Evolving Standards: Proactively monitoring and addressing emerging concerns and regulatory requirements related to the handling, storage and combustion of ammonia in marine environments. This promotes early adaptation and helps avoid costly retrofits later.
- Understanding Regulatory Impact: Anticipating the impact of regulations and proactively planning operations and technologies that are compatible with future regulatory changes.
2. Development and Implementation of a Multifaceted Safety Framework: Given ammonia’s inherent risks, building a strong safety framework is paramount. This involves:
- Qualitative Risk Assessment Through HAZID Studies: Conducting HAZID studies to systematically identify potential hazards related to ammonia throughout its life cycle on board a vessel, from bunkering to combustion. This structured process intends to facilitate the consideration of numerous risk scenarios, which can then inform targeted mitigation strategies
- Quantitative Risk Assessment Through CFD Modeling: Employing CFD dispersion studies to quantitatively assess the potential impact of ammonia releases under various scenarios. These simulations predict vapor concentration and spread, enabling optimized design of ventilation systems, gas detection and emergency response protocols.
3. Real-Time Monitoring and Optimized Emergency Response: A robust system must be in place to detect and rapidly respond to ammonia-related incidents:
- Emergency Response Optimization Through Probabilistic Risk Analysis: This method simulates each step of an emergency plan under different scenarios — such as how an ammonia plume might spread and how people react. Simulating these situations highlights where changes could reduce the chances of injuries and improve emergency response. This information helps improve evacuation strategies and supports better decision-making during emergency planning.
- Early Leak Detection with Advanced Technology: Implementing real-time monitoring systems, such as acoustic cameras, for the rapid and precise detection of ammonia leaks. These technologies facilitate immediate intervention, minimizing potential exposure risks and preventing escalation.
According to ABS, by systematically addressing these three interconnected areas, the maritime industry can confidently transition to ammonia as a cleaner fuel source. This approach will help ensure not only environmental sustainability but also the safe, reliable and efficient operation of ammonia-fueled vessels.
Through detailed analysis of ammonia dispersion studies and emergency evacuation protocols, ABS is contributing to the discourse on safe and supportable maritime fuel alternatives, fostering a culture of preparedness and resilience.
…said Vassilios Kroustallis, Senior Vice President, Global Business Development, ABS.
Content Original Link:
" target="_blank">



































































